
Meta Description:
Learn what a resistor is, how it works, types of resistors, color coding, and practical uses in electronics. A beginner-friendly guide with examples and FAQs to help you master this essential component.
Introduction: What is a Resistor?
Contents
- 1 Introduction: What is a Resistor?
- 2 What is a Resistor?
- 3 How Does a Resistor Work?
- 4 Units of Resistance
- 5 Types of Resistors
- 6 Resistor Color Code: How to Read Resistors
- 7 Why Resistors Are Important
- 8 Practical Uses of Resistors in DIY Electronics
- 9 How to Choose the Right Resistor
- 10 Resistors in Arduino Projects
- 11 FAQs About Resistors
- 12 Conclusion
- 13 Related Posts You May Like:
In the world of electronics, the resistor is one of the most essential and widely used components. Whether you’re building a simple LED circuit or a complex Arduino project, resistors help you control current, protect components, and shape circuit behavior.
But what exactly is a resistor, and how does it work?
In this complete guide, you’ll learn:
- What a resistor is
- How resistors work
- Types of resistors
- Resistor color codes
- Applications in real projects
- And much more!
Let’s dive in.
What is a Resistor?
A resistor is a passive electronic component that resists the flow of electric current. It reduces current, divides voltage, and protects sensitive components in a circuit.
📌 Definition:
A resistor is an electrical component that introduces a specific amount of resistance (measured in ohms, Ω) to an electric current.
📘 Symbol in Circuit Diagrams:
makefileCopyEditUS: —\/\/\/—
EU: —┤├—
How Does a Resistor Work?
Ohm’s Law (V = I × R) explains how resistors work:
- V = Voltage across the resistor (Volts)
- I = Current through the resistor (Amps)
- R = Resistance (Ohms)
When a voltage is applied across a resistor, it limits the amount of current that flows through it based on its resistance value.
Example:
If you apply 5V to a 1kΩ resistor, the current will be:
I = V / R = 5V / 1000Ω = 0.005A = 5mA
Units of Resistance
The standard unit of resistance is the Ohm (Ω).
Other units include:
- Kilo-ohms (kΩ) = 1,000 ohms
- Mega-ohms (MΩ) = 1,000,000 ohms
Types of Resistors
There are many types of resistors, each with different properties and uses. Here are the most common ones:
1. Fixed Resistors
- Carbon Film Resistors: Cheap and commonly used in DIY projects.
- Metal Film Resistors: More precise, used in applications requiring accuracy.
2. Variable Resistors (Potentiometers)
- Resistance value can be adjusted manually.
- Used in volume knobs, dimmers, and sensor calibration.
3. Wire-Wound Resistors
- Made by winding wire around a core.
- High power handling, used in power electronics.
4. Surface Mount Resistors (SMD)
- Small and compact.
- Used in modern compact electronics like phones and laptops.
Resistor Color Code: How to Read Resistors
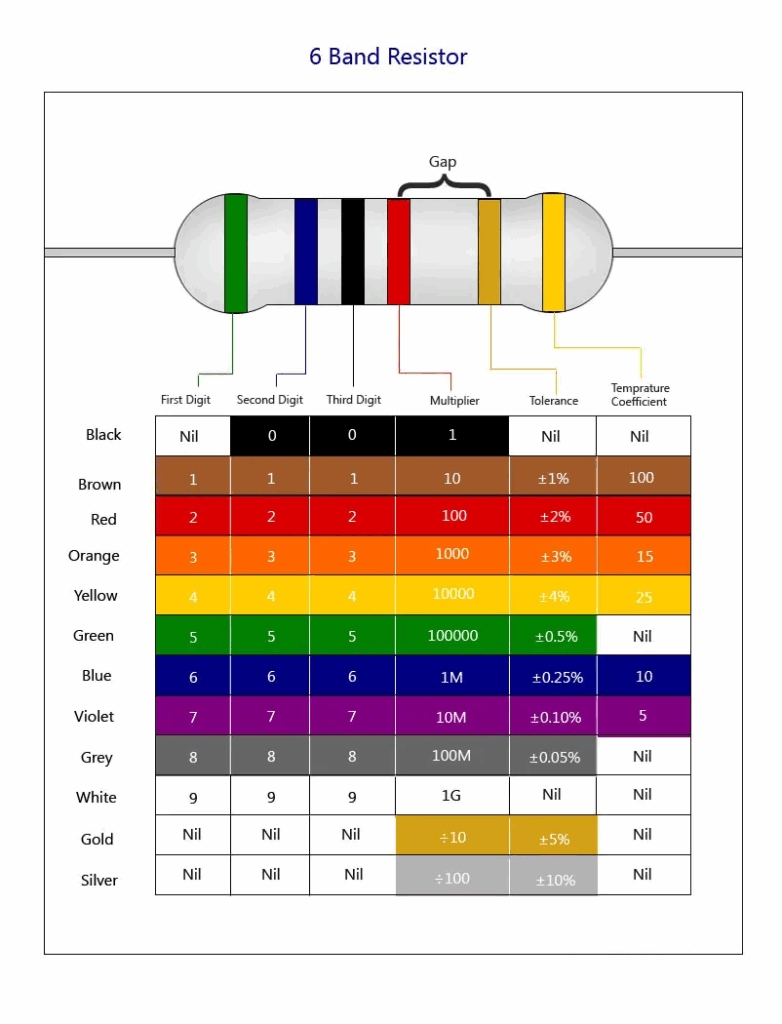
Most resistors have color bands that indicate their resistance value. These bands follow a standard color code:
| Color | Digit | Multiplier |
|---|---|---|
| Black | 0 | x1 |
| Brown | 1 | x10 |
| Red | 2 | x100 |
| Orange | 3 | x1,000 |
| Yellow | 4 | x10,000 |
| Green | 5 | x100,000 |
| Blue | 6 | x1M |
| Violet | 7 | x10M |
| Gray | 8 | x100M |
| White | 9 | x1B |
Example:
A resistor with bands: Red – Violet – Orange – Gold
- Red = 2
- Violet = 7
- Orange multiplier = ×1000
- Gold = ±5% tolerance
So, the resistor value is: 27 × 1000 = 27,000Ω = 27kΩ ±5%
Why Resistors Are Important
Resistors play several vital roles in electronics:
✅ Limit current to protect LEDs and other sensitive parts
✅ Voltage division to create reference voltages
✅ Pull-up/pull-down resistors in digital circuits
✅ Set time constants in RC circuits
✅ Control biasing in amplifiers
Practical Uses of Resistors in DIY Electronics
Here are some real-world examples of where you’d use resistors:
🔹 LED Current Limiting
Without a resistor, an LED may burn out. A 220Ω or 330Ω resistor is commonly used to limit current.
🔹 Pull-Up Resistor for Push Button
In Arduino projects, pull-up resistors (10kΩ) are used to keep input pins at a known voltage level when not pressed.
🔹 Voltage Divider
Two resistors can be used to reduce a voltage — for example, converting 5V to 3.3V.
How to Choose the Right Resistor
When selecting a resistor, consider the following:
1. Resistance Value (Ohms)
Use Ohm’s Law or circuit requirements to determine the correct value.
2. Power Rating (Watts)
Make sure the resistor can handle the power:
P = V × I or P = I² × R
Typical values:
- 1/4W (0.25W) for small circuits
- 1/2W to 1W for higher current
3. Tolerance
Tolerance is the accuracy range:
- Gold = ±5%
- Silver = ±10%
- No band = ±20%
Choose tighter tolerance for precise circuits.
Resistors in Arduino Projects
Resistors are used in nearly every Arduino project. Here are a few examples:
- LED Blink: Use a 220Ω resistor in series with the LED.
- Sensor Interfacing: Use pull-down resistors with PIR sensors.
- Analog Readings: Use resistor voltage dividers for battery level monitoring.
FAQs About Resistors
Q1: What happens if I use the wrong resistor value?
A: Too low = too much current (may damage components); too high = too little current (circuit may not work).
Q2: Can resistors be connected in series or parallel?
A: Yes! In series, resistance adds up. In parallel, total resistance decreases.
Q3: Are resistors polarized?
A: No, resistors can be connected in any direction.
Q4: Can I make a custom resistor value?
A: Yes, by combining resistors in series or parallel.
Q5: Do resistors generate heat?
A: Yes, resistors dissipate electrical energy as heat. Choose a proper power rating to avoid overheating.
Conclusion
Resistors may be small, but they are mighty in functionality. Whether you’re a beginner learning to blink an LED or a pro building complex circuits, resistors are absolutely essential.
By understanding their types, uses, color coding, and proper selection, you can confidently design and troubleshoot electronic circuits.
Related Posts You May Like:
- 🔌 What is a Jumper Wire? Beginner’s Guide
- 💡 How to Blink an LED Using Arduino
- 🔋 Understanding Ohm’s Law for Beginners